Twitter data crunching: The new crystal ball
Fabio Ciulla from Northeastern University, Boston, USA, and his colleagues demonstrated that the elimination of contestants in TV talent shows based on public voting, such as American Idol, can be anticipated. They unveiled the predictive power of microblogging Twitter signals—used as a proxy for the general preference of an audience—in a study recently published in EPJ Data Science.
The authors considered the voting system of these shows as a basic test to assess the predictive power of Twitter signals. They relied on the overlap between Twitter users and show audience to collect extremely detailed data on social behaviour on a massive scale. This approach provided a unique and unprecedented opportunity to apply network science to social media. Social phenomena can thus be studied in a completely unobtrusive way. Previously, Twitter has already been used to forecast epidemics spreading, stock market behaviour and election outcomes with varying degrees of success.
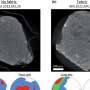
In this study, the authors demonstrated that the Twitter activity during the time span limited to the TV show airing and the voting period following it correlated with the contestants' ranking. As a result, it helped predict the outcome of the votes. This approach offers a simplified version helping to analyse complex societal phenomena such as political elections. Unlike previous voting systems, Twitter offers a quantitative indicator that can act as proxy for what is occurring around the world in real time, thereby anticipating the outcome of future events based on opinions.
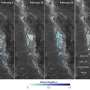
Ciulla and colleagues also showed that the fraction of tweets that included geolocalisation information enabled to internationally map the fan base of each contestant. They identified a strong influence by the geographical origin of the votes, suggesting a different outcome to the show, if voting had not been limited to US voters.
More information: F. Ciulla, D. Mocanu, A. Baronchelli, B. Goncalves, N. Perra, A. Vespignani (2012). Beating the news using Social Media: the case study of American Idol. European Physical Journal Data Science; DOI 10.1140/epjds8
Journal information: European Physical Journal Data Science
Provided by Springer