Researchers discover how bacteria sense salt stress
A team of scientists led by Assistant Professor Ganesh S Anand and Professor Linda J. Kenney from the National University of Singapore (NUS) Department of Biological Sciences (DBS) and the Mechanobiology Institute (MBI) has discovered how bacteria respond to salts in their environment and the ways in which salts can alter the behaviour of specialised salt sensor bacterial proteins.
This novel finding sheds light on how microbes detect levels of salts or sugars in their watery environments – a problem in biology that has been studied for more than 30 years.
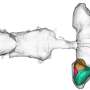
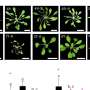
The NUS scientists found that microbes do this by specialised molecules or proteins on the bacterial surface that change shape in response to changes in salt concentration. This is relevant not only to bacteria, but also cells from all organisms which detect and respond to changes in environmental salts and sugars.
The scientists from NUS and the University of Illinois-Chicago (UIC) first published their findings in the EMBO Journal on 30 May 2012.
Bacteria have elaborate mechanisms for sensing and responding to changes in the environment. One of the important environmental stresses for bacteria is the changing concentration of salts. For instance, some can live in fresh water (a low salt environment) or in the guts of humans (high salt environment).
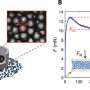
Using a powerful combination of a tool called amide hydrogen/deuterium exchange mass spectrometry (HDXMS), accompanied by molecular biology and biochemistry, the scientists from NUS probed how changes in salt concentrations are sensed by a receptor protein.
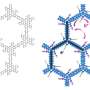
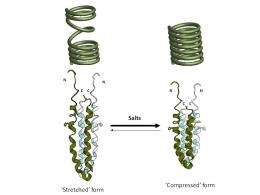
They found that salt detecting proteins are like molecular springs, or "slinky toys". The proteins are constantly shifting from a condensed spring form to an extended form. Increasing the salt concentration dampens this spring-like movement, which activates the protein. In other words, the less spring-like the protein, the higher is its activity. This
This study is an example of basic science with immediate applications. Recognising that diverse proteins operate as molecular springs whose spring-like movement can be dampened is fundamental to understanding how these proteins work. This study also underscores the role of water in biology. It demonstrates how salts and sugars can alter biological properties of proteins through the effects on water and is relevant for understanding life processes across species from bacteria to humans.
The NUS research team is now working on studying the protein in its native membrane by embedding the bacterial sensor protein in an artificial membrane. They hope to understand how the membrane contributes to overall protein activity, structure, stability and responses to salts.
Journal information: EMBO Journal
Provided by National University of Singapore