Astronomers Find Super-Earth Using Amateur, Off-the-Shelf Technology (w/ Video)

(PhysOrg.com) -- Astronomers announced today that they have discovered a "super-Earth" orbiting a red dwarf star 40 light-years from Earth. They found the distant planet with a small fleet of ground-based telescopes no larger than those many amateur astronomers have in their backyards. Although the super-Earth is too hot to sustain life, the discovery shows that current, ground-based technologies are capable of finding almost-Earth-sized planets in warm, life-friendly orbits.
The discovery is being published in the December 17 issue of the journal Nature.
A super-Earth is defined as a planet between one and ten times the mass of the Earth. The newfound world, GJ1214b, is about 6.5 times as massive as the Earth. Its host star, GJ1214, is a small, red type M star about one-fifth the size of the Sun. It has a surface temperature of only about 4,900 degrees F and a luminosity only three-thousandths as bright as the Sun.
GJ1214b orbits its star once every 38 hours at a distance of only 1.3 million miles. Astronomers estimate the planet's temperature to be about 400 degrees Fahrenheit. Although warm as an oven, it is still cooler than any other known transiting planet because it orbits a very dim star.
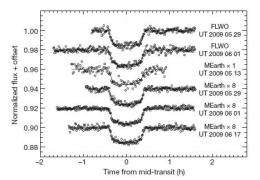
Since GJ1214b crosses in front of its star, astronomers were able to measure its radius, which is about 2.7 times that of Earth. This makes GJ1214b one of the two smallest transiting worlds astronomers have discovered (the other being CoRoT-7-b). The resulting density suggests that GJ1214b is composed of about three-fourths water and other ices, and one-fourth rock. There are also tantalizing hints that the planet has a gaseous atmosphere.
"Despite its hot temperature, this appears to be a waterworld," said Zachory Berta, a graduate student at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA) who first spotted the hint of the planet among the data. "It is much smaller, cooler, and more Earthlike than any other known exoplanet."
Berta added that some of the planet's water should be in the form of exotic materials like Ice VII (seven) - a crystalline form of water that exists at pressures greater than 20,000 times Earth's sea-level atmosphere.
Astronomers found the new planet using the MEarth (pronounced "mirth") Project - an array of eight identical 16-inch-diameter RC Optical Systems telescopes that monitor a pre-selected list of 2,000 red dwarf stars. Each telescope perches on a highly accurate Software Bisque Paramount and funnels light to an Apogee U42 charge-coupled device (CCD) chip, which many amateurs also use.

"Since we found the super-earth using a small ground-based telescope, this means that anyone else with a similar telescope and a good CCD camera can detect it too. Students around the world can now study this super-earth!" said David Charbonneau of CfA, lead author and head of the MEarth project.
MEarth looks for stars that change brightness. The goal is to find a planet that crosses in front of, or transits, its star. During such a mini-eclipse, the planet blocks a small portion of the star's light, making it dimmer. Using innovative data processing techniques, astronomers can tease out the telltale signal of a transiting planet and distinguish it from "false positives" such as eclipsing double stars.
NASA's Kepler mission also uses transits to look for Earth-sized planets orbiting Sun-like stars. However, such systems dim by only one part in ten thousand. The higher precision required to detect the drop means that such worlds can only be found from space.
In contrast, a super-Earth transiting a small, red dwarf star yields a greater proportional decrease in brightness and a stronger signal detectable from the ground. Astronomers then use instruments like the HARPS (High Accuracy Radial Velocity Planet Searcher) spectrograph at the European Southern Observatory to measure the companion's mass and confirm it is a planet, as they did with this discovery.
When astronomers compared the measured radius of GJ1214b to theoretical models, they found that the observed radius exceeds the model's prediction, even assuming a pure water planet. Something more than the planet's solid surface may be blocking the star's light - specifically, a surrounding atmosphere.
The team also notes that, if it has an atmosphere, those gases are almost certainly not primordial. The star's heat is gradually boiling off the atmosphere. Over the planet's multiple-billion-year lifetime, much of the original atmosphere may have been lost.

The next step for astronomers is to try to directly detect and characterize the atmosphere, which will require a space-based instrument like NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. GJ1214b is only 40 light-years from Earth, within the reach of current observatories.
"Since this planet is so close to Earth, Hubble should be able to detect the atmosphere and determine what it's made of," said Charbonneau. "That will make it the first super-Earth with a confirmed atmosphere - even though that atmosphere probably won?t be hospitable to life as we know it."
More information: Nature: "A Super-Earth Transiting a Nearby Low-Mass Star", by David Charbonneau et al.
Provided by Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics