'NanoPen' may write new chapter in nanotechnology manufacturing
Researchers in California are reporting development of a so-called "NanoPen" that could provide a quick, convenient way of laying down patterns of nanoparticles — from wires to circuits — for making futuristic electronic devices, medical diagnostic tests, and other much-anticipated nanotech applications. A report on the device, which helps solve a long-standing challenge in nanotechnology, appeared in ACS' Nano Letters.
In the new study, Ming Wu and colleagues point out that researchers have already developed several different techniques for producing patterns of nanoparticles, which are barely 1/50,000th the width of a human hair. But current techniques tend to be too complex and slow. They require bulky instrumentation and take minutes or even hours to complete.
These techniques also require the use of very high temperatures to apply the nanostructures to their target surfaces. Such limitations prevent widespread application of such techniques, the researchers say.
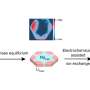
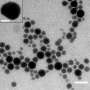
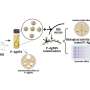
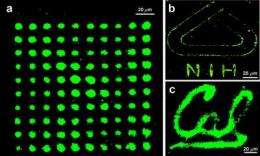
The scientists say their NanoPen solves these problems. In lab studies, the researchers used it to deposit various nanoparticles into specific patterns in the presence of relatively low light and temperature intensities. The process, which requires the use of special "photoconductive" surfaces, takes only seconds to complete, they note.
Manufacturers can adjust the size and density of the patterns by adjusting the voltage, light intensity, and exposure time applied during the process, the researchers say.
More information: "NanoPen: Dynamic, Low-Power, and Light-Actuated Patterning of Nanoparticles," Nano Letters
Source: American Chemical Society (news : web)