Grid helps find one picture in a million
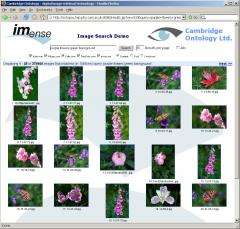
(PhysOrg.com) -- Looking for images on the internet can be a frustrating business. Whether you want the perfect sunset over the sea or the London skyline by night, youre dependent on people to describe the images on their web pages. Now Imense Ltd, a high-tech Cambridge start-up, has announced new investment to help them become the Google of image searching, using their revolutionary technology.
To test their software, they've made an unexpected partnership with a group of particle physicists using a massive computer Grid.
Professor Keith Mason, Chief Executive of the Science and Technology Facilities Council (STFC) describes how this happened "We actively encourage the researchers we fund to consider the wider applications of the work they do. In this case, computing problems that had to be addressed for particle physics can also be used to solve other challenges with large amounts of data. The Council's Knowledge Exchange Service put the two teams together and provided modest funding to start them off - the new investment attracted by Imense represents a ten-fold return on the initial development funds."
Images and video make up over 70% of the digital data available on the Internet, an estimated 15 billion images, but traditional search engines can't index this information directly, instead relying on text descriptions entered by hand. Imense's key innovation is a new form of image retrieval that automatically analyses images in terms of their content, without the need for human generated captions. They have also developed a powerful query language that lets people search for the images they need.
Dr David Sinclair, one of the founders of Imense Ltd, explains, "We built a prototype of our new image analysis and search technology, but simply weren't able to test our software on sufficiently large numbers of photos. We knew we could search tens of thousands of pictures, but couldn't afford to try it on hundreds of thousands or millions of images. This made it difficult for Imense to get the investment we needed to develop a commercially viable product. That's where our partnership with the particle physics Grid came in."
Spread across 17 sites, the UK particle physics Grid (GridPP) has been built to analyse the petabytes of data expected from Europe's newest particle accelerator, the Large Hadron Collider. But its 8000 computers have also been shared with other researchers, from geophysicists to biologists. Last year, Sinclair attended a meeting arranged by STFC about Grid opportunities for industry, and realized that Grid technology could be the answer to Imense's problem. Image analysis is a naturally parallel process which fits perfectly with the capabilities of the Grid used by STFC scientists to process data in particle physics.
Professor Andy Parker, Director of the eScience Centre, University of Cambridge, led the particle physics team working with Imense, "Our team helped Imense develop their software to run on the Grid using a tool called Ganga, and supported them as they analysed three million images. We also dealt with issues such as security and working with Grid managers at other universities, who were very helpful. It went very smoothly and was fascinating to see the company start-up process in action."
Imense have now reaped the rewards of their Grid experience, with an investment of more than £500,000 to help them bring a product or service to market in the coming months.
Dr Sinclair says that the Grid played a major role in this, "Our work with the Grid has let us demonstrate that our software can handle millions of images, at a time when we were a small company and couldn't supply the computing power needed ourselves. This in turn impressed the investors we spoke to, and led to funding for our company." Imense plans to use the open source Grid technologies from the particle physics domain in its commercial product.
Provided by Science and Technology Facilities Council