Ultra-fine coatings on sediment grains influence nitrate and sulfate storage in soil
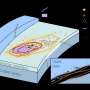
Tiny sediment grains are covered with a very fine-grained, complex mixture of minerals in an open fabric that results in a large surface area in contact with water between the grains. Scientists at the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) are studying this microscopic layer and finding that the mineral composition of these coatings on sediment grains in the unsaturated zone (i.e., between land surface and the water table) can have a substantial effect on the retention of nitrate and sulfate.
Their findings are particularly important for evaluating the long-term effects of agriculture on water quality, as the storage of these common components of fertilizer in the unsaturated zone can affect the quality of shallow groundwater for many years after fertilizer application ceases.
Nitrate and sulfate are important plant nutrients. Farmers and soil scientists routinely monitor the nutrient content of the soil in farm fields so that fertilizer application can be managed to maintain profitability and to minimize runoff or infiltration. Loss of excess nutrients can elevate levels in streams and shallow groundwater. Understanding the mechanisms of nutrient storage in the unsaturated zone is critical to protecting groundwater resources.
Timothy Reilly, the lead author of the study, stated "The unsaturated zone is potentially a large reservoir for anions (negatively charged ions) like nitrate and sulfate. The increased residence time indicated by these findings suggests that models in areas with similar mineral characteristics, which neglect or minimize storage, will not accurately predict nutrient transport to the water table."
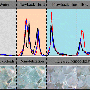
In the study, unsaturated-zone sediments and the chemistry of shallow groundwater underlying a small (about 3 square miles) watershed in southern New Jersey were studied to identify mechanisms responsible for nutrient storage. Lower unsaturated zone sediments and shallow groundwater samples were collected at 11 locations, and concentrations of nitrate and sulfate were determined. Nutrient storage in the very fine-grained mineral coatings on the sediment grains was attributed to a complex combination of chemical and physical storage mechanisms.
Results from the study, supported by the US Geological Survey Toxic Substances Hydrology Program, were published in the February 2009 issue of the Vadose Zone Journal. The research was also presented in Houston, TX at the joint annual meeting of the Geological Society of America and Soil Science Society of America in October 2008. These findings are particularly important for evaluating the long-term effects of agricultural land use on groundwater quality. Continuing research includes characterizing stream sediments, determining relations between sediment mineralogy and the concentration of pesticides stored on the sediments, and laboratory experiments evaluating storage mechanisms.
More information: vzj.scijournals.org/cgi/content/full/8/1/75
Source: Soil Science Society of America