Tailored for optical applications
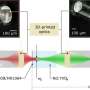
When a calcite crystal is placed onto a printed page, the letters appear doubled. This is the result of a property called birefringence. Scientists at the Simon Fraser University in Canada have now developed a material that is among the most birefringent solids ever observed. As described in the journal Angewandte Chemie, this material is not a mineral, but rather a coordination polymer.
Refraction is the change in direction of a wave of light when it passes from air into water or a crystal. It is caused by a local change in the speed of propagation. In the case of birefringence, the light is divided into two perpendicularly polarized beams, which move at different speeds and exit the material shifted relative to each other. The source of this effect is a crystal lattice that has different optical properties along its various axes (anisotropy).
Birefringent optical components are usually made of calcite. The critical value for these applications is the difference in the refractive index of light in two directions in the crystal, the birefringence, which is 0.17 for calcite.
The team led by Daniel B. Leznoff and Zuo-Guang Ye has now produced a highly birefringent coordination polymer. Coordination polymers are one-, two-, or three-dimensional bridged metal complexes. The advantage to this type of compound is the limitless number of design possibilities: The individual components—metal center, chelating ligands, and bridging ligands—can be selected and combined almost at will to get the desired material properties.
Leznoff’s team, spearheaded in the lab by Michael J. Katz, decided to use a “terpy” ligand, a flat ring system consisting of three pyridine units (six-membered aromatic rings with one nitrogen atom), and lead as the metal center. The complexes are linked by linear bridging ligands made of a central silver or gold ion and two cyanide groups to form two-dimensional layers. If the central lead atom is replaced with manganese, one-dimensional ladder-like structures are formed. Within their crystals, however, the lead and manganese polymers have analogous arrangements: the terpy molecules are piled up plane-to-plane, perpendicular to the axis of crystal growth. This is clearly the crucial factor leading to the high birefringence, which reaches values from 0.43 to just under 0.4, significantly higher than those of the numerous inorganic birefringent materials.
Improved optical data storage and data transfer in communications technology are possible applications for such highly birefringent materials.
Source: Wiley